Thermal spraying is a surface engineering technique used to add or to restore functionality to a functional surface by applying a specifically designed and engineered coating. Examples of coating functionality include protection against wear, erosion, abrasion or heat.
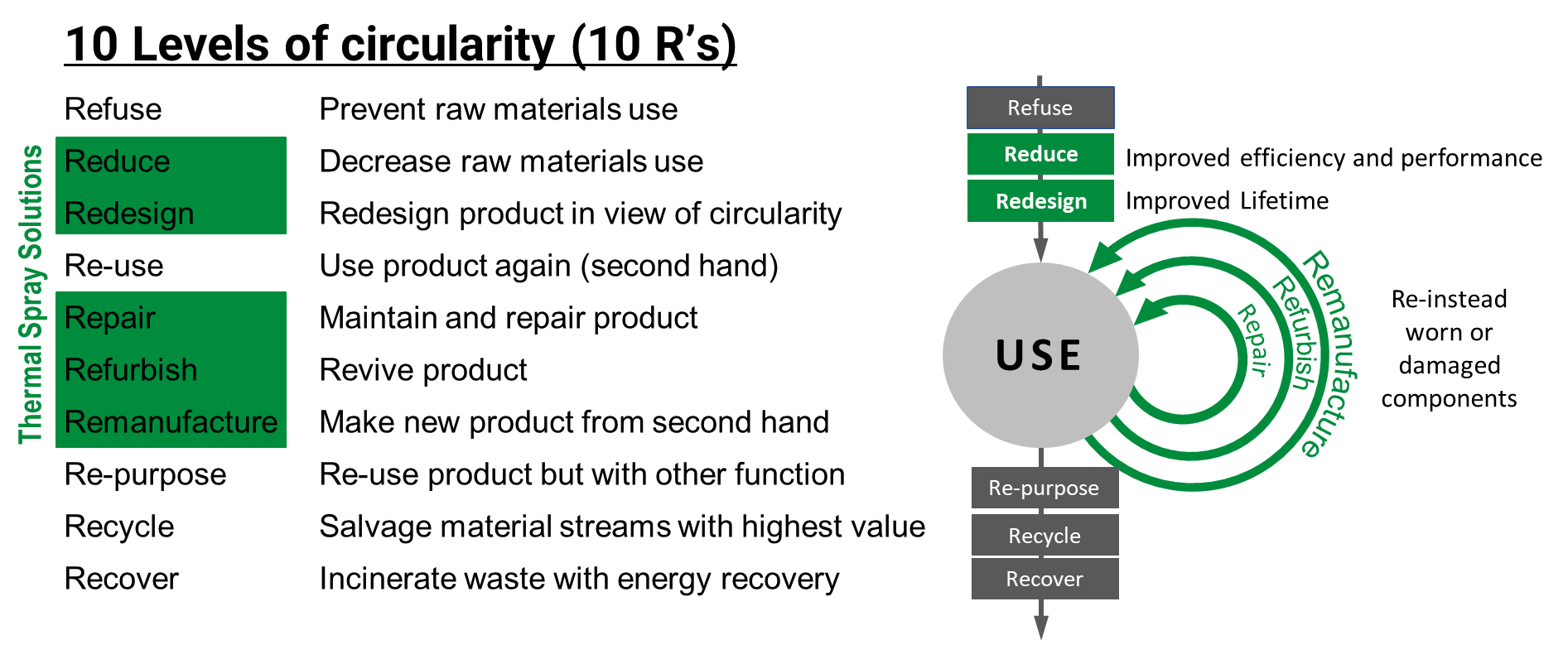
There are a number main areas of thermal spray adding value to sustainable products:
- Repair, refurbish and remanufacture (Re-use worn and damaged components)
- Reduce (Improved efficiency and performance)
- Redesign (Improved Lifetime)
Being a surface technique, thermal spraying limits the use of expensive, material resources and energy consumption used to manufacture bulk material; and in turn offers improved customized surface characteristics to improve and enhance the life, efficiency and/or performance of a component. The thermal spray process by its nature already contributes to the reduction of global warming by enabling restore and repair, and improve lifetime, efficiency and performance.
In terms of its contribution to the cause of global warming, thermal spraying stands in sharp contrast to the energy-intensive processes such as melting, casting, extrusion and welding.
Repair, refurbish and remanufacture; ADDING VALUE TO A CIRCULAR ECONOMY
We all have known for a while that our resources are not endless. There is only so much more in the world to be mined or trees that can be harvested without causing short- and long-term environmental effects. Implementing the principles of a circular economy ensures that we make the most of the resources we are already using and protecting our ecosystems from overuse.

Along with environmental responsibility, we also face social and economic responsibility.
Increase the number of value retention processes
In order to achieve a circular economy in manufacturing specifically, we have to begin looking at value retention processes. Value retention processes are methods that retain value in the system by adding value and utility to a product and/or extending the useful life of a product beyond its expected end-of-use. This includes practices such as choosing repair and overhaul over buying new or purchasing remanufactured equipment as opposed to new. A great example of circular economy would be instead of buying a new pump, buying a pump with remanufactured components.
Thermal spray can be used for the value retention process. Thermal spray repair applications can reduce waste by repairing damaged machine parts. Thermal spray coatings can keep machine parts in use longer by increasing wear and corrosion resistance. Thermal spray can also be repeated over and over allowing you to reuse the same machine parts again and again.
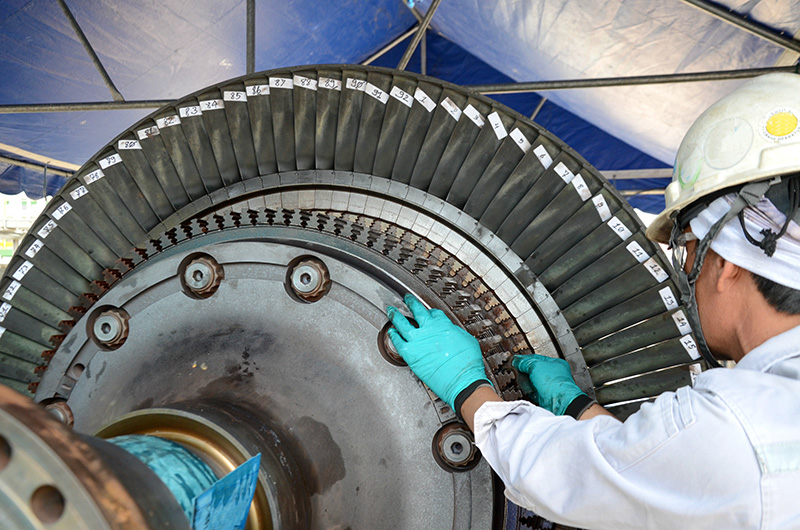

Reduce – Improved efficiency and performance
On other way to make a contribution to a sustainable future is to make systems operate more efficiently. One of the most widely used coatings to increase efficiency are abradable coatings used in Jet Engines and turbochargers. These coatings can increase efficiency by 1-3%, which saves millions of liters of fuel per day on a global scale, which in turn results in major reductions in CO2 and NOX emissions.
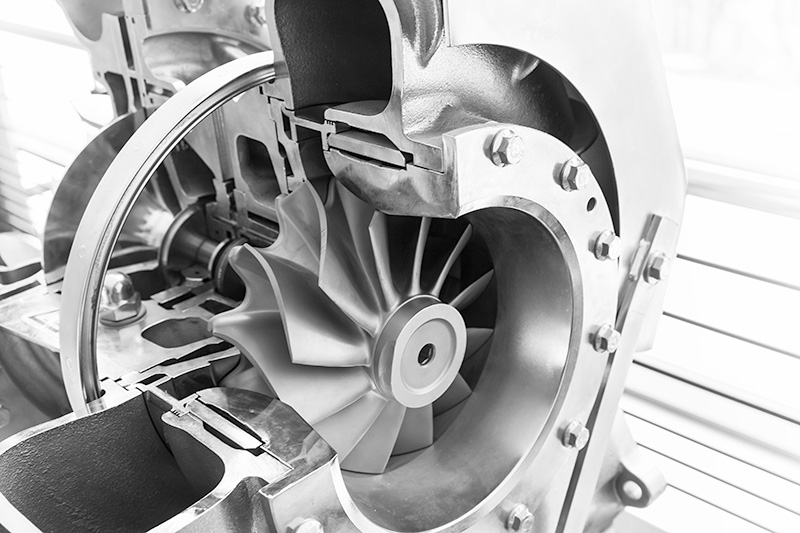

Another great example is the Cylinder Liner Coatings for combustion engines. Coatings applied to cylinder bores result in low friction, low oil and fuel consumption, reduced wear and increased corrosion resistance and on a whole 2% to 4% fuel savings reported.
Redesign - Improved Lifetime
Components or products have a lifetime. Extending the lifetime of a component or product is obvious choose to reduce waste (scrapping a part) or saving energy (remanufacturing a part). The Thermal Spray Technology has countless application/examples of a coating increasing lifetime by sometimes up to 10x or more.
An example: Wind power installations have to work in sun, rain, snow and wind. Those located offshore must also contend with salt, which poses a constant threat of corrosion. Special materials and surface solutions increase lifetime by the protection against wear, corrosion and fatigue. One example is transmission gears, which are subjected to up to 144 million revolutions of the rotor shaft, or 15 billion revolutions of the generator shaft, during their service life.
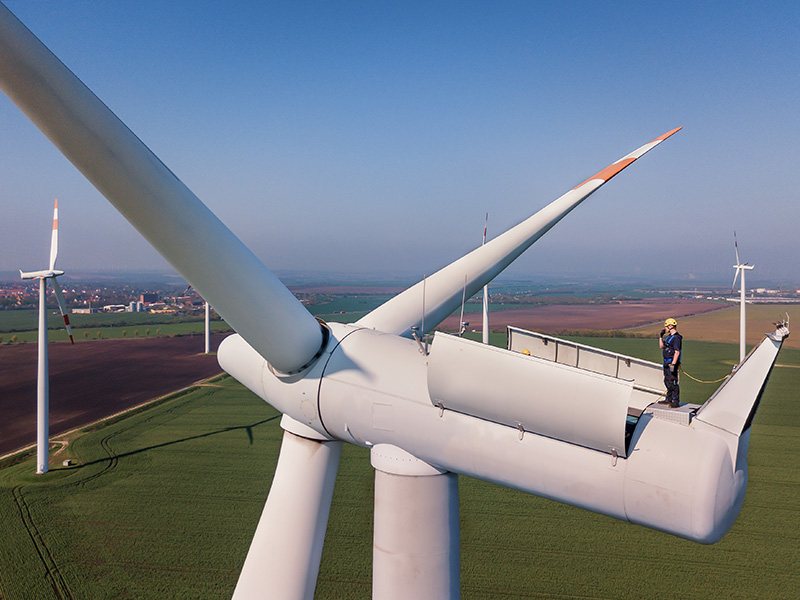

Some other of the main areas of applications include:
- Wear Resistance
- Examples
- Corrosion Resistance
- Heat Resistance (aging)
- Examples
- Industrial Gas Turbines
- Jet Engines
- Cylinder Heads
- Examples

CONCLUSION
Thermal Spray Coatings have been around for many years and the number of applications have been growing ever since. In the past but also now they are mainly used for the 3 reasons listed:
- Repair, refurbish and remanufacture (Re-use worn and damaged components)
- Reduce (Improved efficiency and performance)
- Redesign (Improved Lifetime)
Not only are these reasons providing economic benefits, they also greatly contribute to energy and this CO2 reductions.
For more information, please contact your FST Representative
